概述
官方文档:https://github.com/weibocom/motan/wiki/zh_userguide
register 模块
用来和注册中心进行交互,包括注册服务、订阅服务、服务变更通知、服务心跳发送等功能;Server 端会在系统初始化时通过 register 模块注册服务,Client 端在系统初始化时会通过 register 模块订阅到具体提供服务的 Server 列表,当 Server 列表发生变更时也由 register 模块通知 Client。
protocol 模块
用来进行 RPC 服务的描述和 RPC 服务的配置管理,这一层还可以添加不同功能的 filter用来完成统计、并发限制等功能。
serialize 模块
将 RPC 请求中的参数、结果等对象进行序列化与反序列化,即进行对象与字节流的互相转换;默认使用对 Java 更友好的 hessian2 进行序列化。
transport 模块
用来进行远程通信,默认使用 Netty NIO 的 TCP 长链接方式。
cluster 模块
Client 端使用的模块,cluster 是一组可用的 Server 在逻辑上的封装,包含若干可以提供 RPC 服务的 Server,实际请求时会根据不同的高可用与负载均衡策略选择一个可用的 Server 发起远程调用。
在进行 RPC 请求时,Client 通过代理机制调用 cluster 模块,cluster 根据配置的 HA 和 LoadBalance 选出一个可用的 Server,通过serialize模块把RPC请求转换为字节流,然后通过 transport 模块发送到 Server 端。
配置元素
Motan 框架中将功能模块抽象为四个可配置的元素,分别为:
protocol:服务通信协议。服务提供方与消费方进行远程调用的协议,默认为 Motan 协议,使用 hessian2 进行序列化,Netty 作为 Endpoint 以及使用Motan 自定义的协议编码方式。
registry:注册中心。服务提供方将服务信息(包含IP、端口、服务策略等信息)注册到注册中心,服务消费方通过注册中心发现服务。当服务发生变更,注册中心负责通知各个消费方。
service:服务提供方提供的服务。使用方将核心业务抽取出来,作为独立的服务。通过暴露服务并将服务注册至注册中心,从而使调用方调用。
referer:服务消费方对服务的引用,即服务调用方。
Motan 推荐使用 Spring 配置 RPC 服务,目前 Motan 扩展了 6 个自定义 Spring XML 标签
motan:protocol
motan:registry
motan:basicService
motan:service
motan:basicReferer
motan:referer
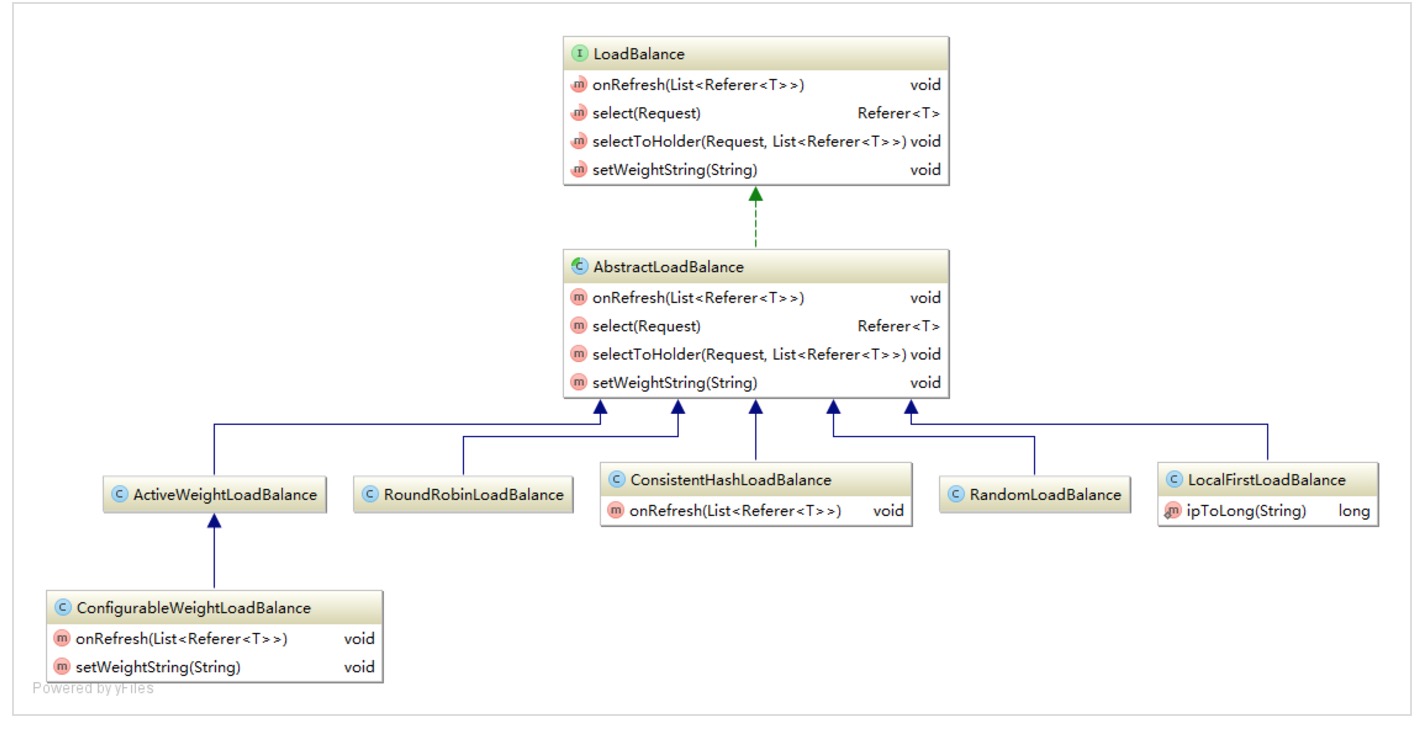
高可用方面是 Motan 的一大特点,支持多种服务治理和高可用机制,包括:灵活多样的集群负载均衡策略,支持 ActiveWeight/Random/RoundRobin/LocalFirst/Consistent等6种策略,并支持自定义扩展;
自动集成Failover、Failfast容错策略,实现故障节点自动摘除,自动探测恢复,有效进行服务故障隔离,远离服务卡死及雪崩;
连接池自定义控制,根据业务场景灵活配置;支持多机房间调用流量压缩、动态流量调整,实现真正的跨 IDC 的高可用。基于高并发、高负载场景的优化,具备在高压力场景下的高可用能力。
郑大侠的笔记 motan
http://code.zhizus.com/categories/Motan%E6%BA%90%E7%A0%81%E8%A7%A3%E8%AF%BB/
Motan源码解读-SPI机制
SPI 全称为 (Service Provider Interface) ,是JDK内置的一种服务提供发现机制。
java的spi就是提供这样的一个机制:为某个接口寻找服务实现的机制。有点类似IOC的思想,就是将装配的控制权移到程序之外,在模块化设计中这个机制尤其重要。
Motan源码解读-Client异步消息
接下来我们总结一下motan中callbackMap的逻辑:
client发送request前,先将request注册到(register)到callbackMap中,如果发送前连接异常,则直接remove掉。客户端收到response后,根据requestId找到对应的request上下文,并移除callbackMap中的对应的对象。对于服务端超时或者其他异常,客户端收不到消息的情况,则通过TimeoutMonitor来定时扫描callbackMap来清理。
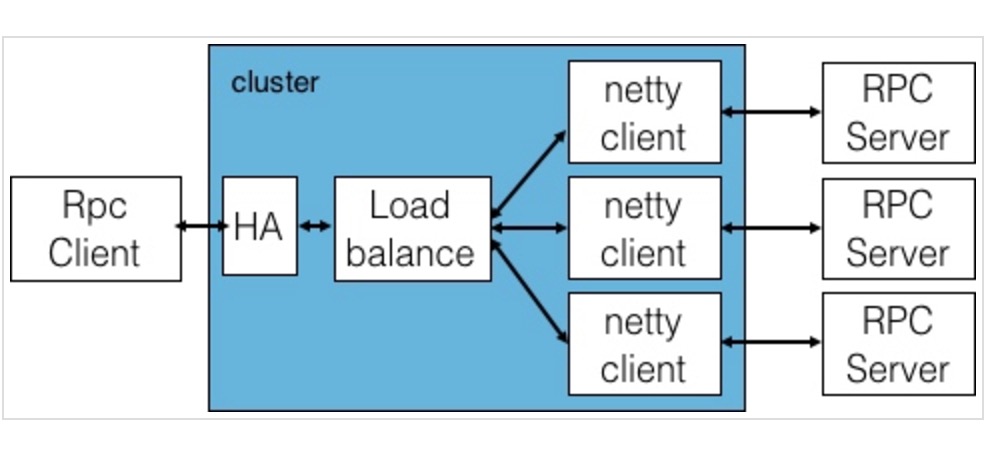
Motan源码解读-负载均衡
RPCClient首先会经过一层HA(这里motan实现了两种容灾策略,failfast&failover),然后会根据配置的loadbalance的策略选取相应的nettyClient发送请求到RPCServer。
// 可以基于SPI扩展,使用方可以实现自己的LoadBalance
@Spi(scope = Scope.PROTOTYPE)
public interface LoadBalance<T> {
//当可用的应用列表变化时会调用这个方法刷新(motan的可用引用列表是基于服务发现这种模式实现,目前实现了consul&zk)
void onRefresh(List<Referer<T>> referers);
// 基于负载均衡的策略选择可用的引用
Referer<T> select(Request request);
// FailoverHaStrategy会使用到这个,多线程场景
void selectToHolder(Request request, List<Referer<T>> refersHolder);
// ?? 仅仅属于WeightLoadBalance的特性,定义在最上层接口是否合适??
//cluster.getLoadBalance().setWeightString(weights); 这里使用的时候判断一下类型,对WeightLoadBalance这种类型单独处理向下转型是否可以?
// 或者是否有其他更好的办法??
void setWeightString(String weightString);
}
Motan源码解读-容错策略
Motan源码解读-Protocol
provider:
服务提供方,通常可以认为是server端
export:
服务提供Provider暴露出去就变成Exporter,服务使用方(客户端)可以调用暴露出去的Provider。
根据URL将exporter从map中取出来,然后,将provider放到exporter中去,然后,再将 exporter放到map中去。
refer:
引用服务,引用的服务会通过配置去调用服务端暴露的服务
Motan源码解读-源码结构
motan-benchmark // 压测相关
motan-core //motan核心代码,也是源码解析的主要包
motan-demo // 示例,快速上手的最佳方法
motan-extension // 扩展
motan-manager // 管理后台
motan-registry-consul //基于consul的服务发现实现
motan-registry-zookeeper // 基于zookeeper的服务发现实现
motan-springsupport // spring容器的支持,也支持springboot
motan-transport-netty // netty传输的封装
Motan源码解读-Filter
很多服务都有filter这个概念,filter就像在管道前的过滤器,只要通过管道的请求必须先经过过滤器。过滤器可以做很多事情,类似权限控制,限流,统计,上报,监控等等。有些为服务架构会把filter单独抽出来作为getway服务
Motan源码解读-codec
motan的codec负责rpc框架通讯协议的编解码。
manager 模块的启动
1.在顶层install 然后,在 manager项目中打包 war包 ,使用 package 命令 。
2.用tomcat启动项目。
motan 的启动
motan_demo_server.xml中: xmlns:motan=”http://api.weibo.com/schema/motan“
spring.handlers中:
http\://api.weibo.com/schema/motan=com.weibo.api.motan.config.springsupport.MotanNamespaceHandler
1.获取命名空间uri :
com.weibo.api.motan.config.springsupport.MotanNamespaceHandler
public class MotanNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
public final static Set<String> protocolDefineNames = new ConcurrentHashSet<String>();
public final static Set<String> registryDefineNames = new ConcurrentHashSet<String>();
public final static Set<String> basicServiceConfigDefineNames = new ConcurrentHashSet<String>();
public final static Set<String> basicRefererConfigDefineNames = new ConcurrentHashSet<String>();
@Override
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("referer", new MotanBeanDefinitionParser(RefererConfigBean.class, false));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("service", new MotanBeanDefinitionParser(ServiceConfigBean.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("protocol", new MotanBeanDefinitionParser(ProtocolConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("registry", new MotanBeanDefinitionParser(RegistryConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("basicService", new MotanBeanDefinitionParser(BasicServiceInterfaceConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("basicReferer", new MotanBeanDefinitionParser(BasicRefererInterfaceConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("spi", new MotanBeanDefinitionParser(SpiConfigBean.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation", new MotanBeanDefinitionParser(AnnotationBean.class, true));
Initializable initialization = InitializationFactory.getInitialization();
initialization.init();
}
}
2.通过反射机制实例化,调用init();方法。
方法中注册了Motan自定DOM节点的解析器
MotanNamespaceHandler继承了NamespaceHandlerSupport。所以不用实现所有的解析工作,只需将自定义schema中的元素解析器注册进来就可以。(schema拓展的解析器)
MotanBeanDefinitionParser(Class<?> beanClass, boolean required);//元素解析器
public class MotanBeanDefinitionParser implements BeanDefinitionParser{
}
3.将实例存入handlerMappings用于后续的解析
4.找到对应DOM节点的解析器,开始解析,
根据MotanNamespaceHandler中注册的信息,spring找到解析类并调用解析方法:MotanBeanDefinitionParser.Parse()。
第一步,初始化RootBeanDefinition
第二步,获取beanid
第三步,将xml中配置的信息放到beandefinition的PropertyValues中。
bd.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("id", id);
最后将BeanDefinition返回出来。配置成bean的类会定义成BeanDefinition,注册到spring。
5.registerBeanPostProcessors();
控制台输出结果
MotanNamespaceHandler 中的init()方法 start
AllSpiInitialization init.
AllSpiInitialization init finish.
MotanNamespaceHandler 中的init()方法 end
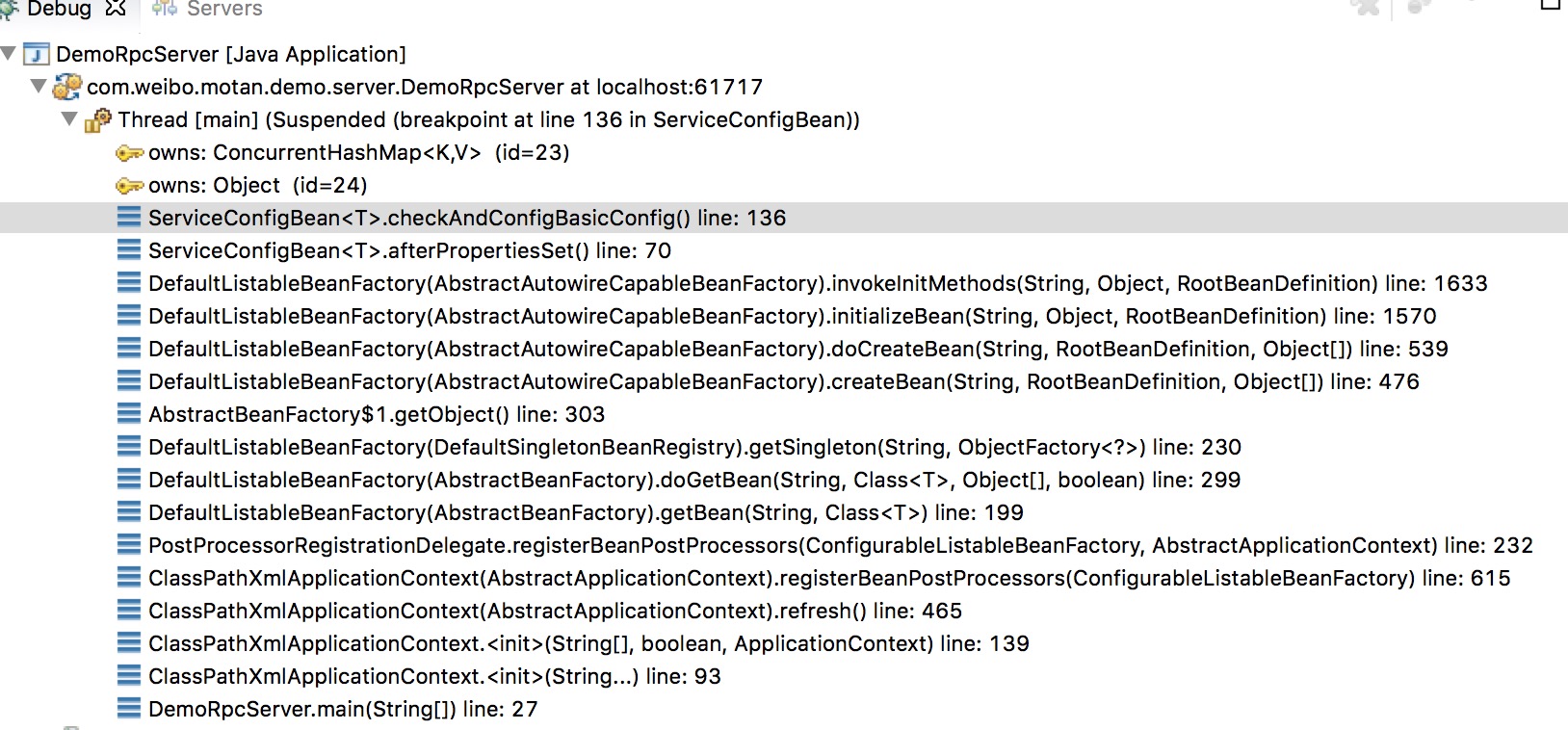
ServiceConfigBean 中 afterPropertiesSet() 方法 start
ServiceConfigBean 中 checkAndConfigBasicConfig 方法 basicServiceConfigDefineNames 集合中的size :1
ServiceConfigBean 中 checkAndConfigBasicConfig 方法 basicServiceConfigDefineNames 集合中的name :serviceBasicConfig
ServiceConfigBean 中 checkAndConfigBasicConfig 方法
ServiceConfigBean 中 checkAndConfigExport 方法 String p : demoMotan
ServiceConfigBean 中 afterPropertiesSet() 方法 end
ServiceConfigBean 中 afterPropertiesSet() 方法 start
ServiceConfigBean 中 checkAndConfigBasicConfig 方法 basicServiceConfigDefineNames 集合中的size :1
ServiceConfigBean 中 checkAndConfigBasicConfig 方法 basicServiceConfigDefineNames 集合中的name :serviceBasicConfig
ServiceConfigBean 中 checkAndConfigBasicConfig 方法
ServiceConfigBean 中 checkAndConfigExport 方法 String p : demoMotan
ServiceConfigBean 中 afterPropertiesSet() 方法 end
ServiceConfigBean 中onApplicationEvent方法:export(); start
AbstractInterfaceConfig 中checkInterfaceAndMethods()方法
AbstractInterfaceConfig 中 loadRegistryUrls() registries的size():1*****以及name:registry
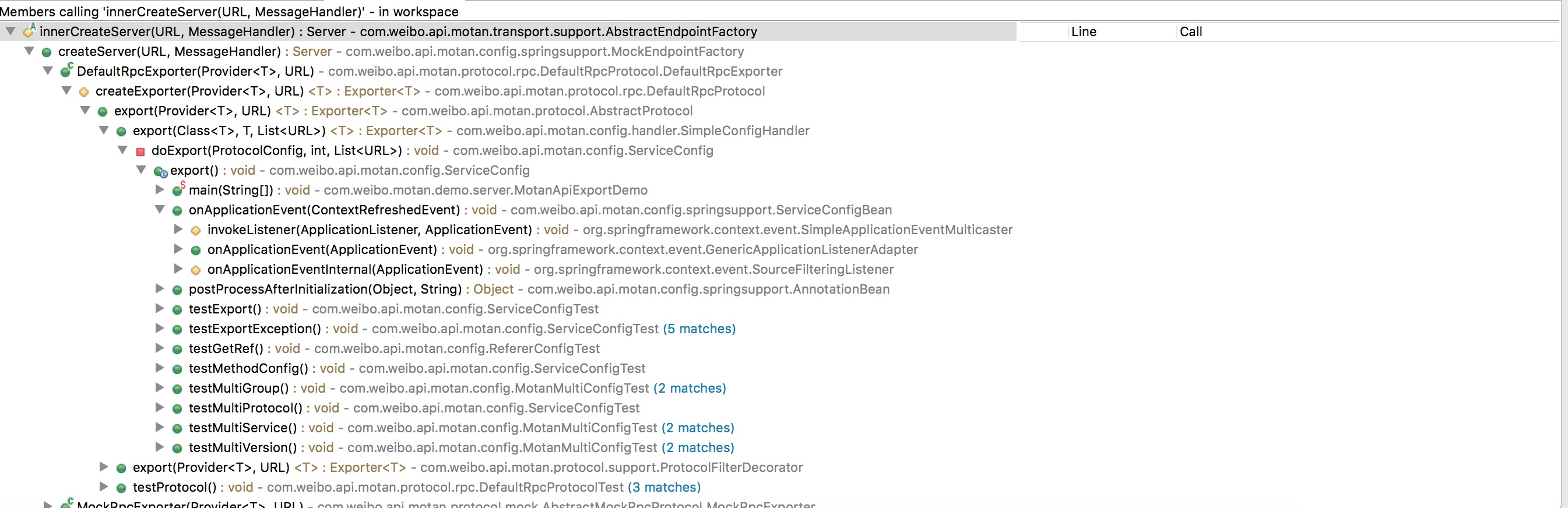
ServiceConfig 中的 export():doExport(protocolConfig, port, registryUrls); strat
SimpleConfigHandler 中 export方法: Exporter<T> exporter = protocol.export(provider, serviceUrl); start
exporter = createExporter(provider, url); 开始
NettyEndpointFactory create share_channel server: url={}motan://10.1.195.135:8001/com.weibo.motan.demo.service.MotanDemoService?group=motan-demo-rpc
AbstractServer 的构造方法
createServer end
exporter = createExporter(provider, url); 结束
exporter.init(); 开始
AbstractNode init()
DefaultRpcProtocol中 DefaultRpcExporter doInit()
public synchronized boolean open()中NettyServer ServerChannel start Open: url=motan://10.1.195.135:8001/?group=motan-demo-rpc
result:true
exporter.init(); 结束
SimpleConfigHandler 中 export方法: Exporter<T> exporter = protocol.export(provider, serviceUrl); end
doExport结束
ServiceConfig 中的 export():doExport(protocolConfig, port, registryUrls); end
ServiceConfigBean 中onApplicationEvent方法:export(); end
...(另一个service)
server start...